What are GST procedures? – GST online registration in Coimbatore
What are GST procedures?
Goods and Service Tax (GST) is structured for reduction in corruption, efficient tax collection, inter-state movement of goods becoming easier and a lot more.
Under GST law, it provides self-assessment to facilitate for payment of taxes and an easy compliance. It also explains about the notices, demand and recovery provisions when the taxes are short paid, unpaid or returns not filed.
GST procedure can be broadly classified as
- Audits
- Assessment
- Demand and Recovery
- Advance Ruling
Audits:
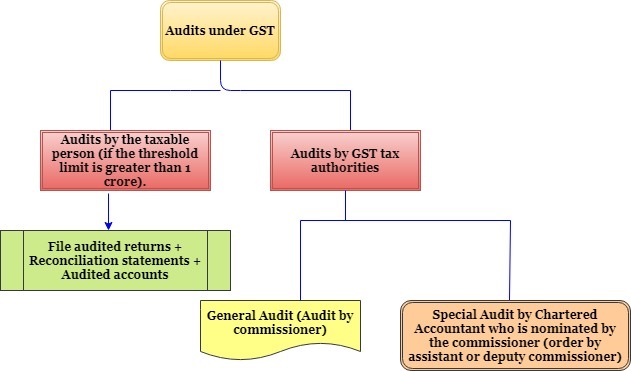
Registered dealer maintains the examination record which is an audit under GST. The main aim is to verify the correctness of information which has been declared, assess the compliance with GST and the taxes paid.
Audit by registered dealer:
Every registered dealer whose turn over during a financial year which exceeds Rs.1 crore has to get his accounts audited by Certified Management Accountant or a Chartered Accountant will be appointed to conduct an audit.
Audit by GST tax authorities:
General Audit:

The commission or by his order, an officer may conduct an audit of any registered dealer.
Special Audit:

The department may conduct a special audit due to the complexity of case and considers the interest of revenue. The CMA or CA will be appointed in order to conduct the audit.
Assessment:
Assessment is referred as the determination of tax liability under GST. This can be divided into 5 types. They are as follows:
- Self-Assessment.
- Provisional Assessment.
- Scrutiny Assessment.
- Summary Assessment.
- Best-Judgement Assessment.
Self-Assessment:

Every registered taxable person as under GST shall assess the taxes which are payable by them on their own, furnish a return for each tax period. This is what we called as self-assessment.
Provisional Assessment:
A registered dealer can request to officer for provisional assessment if he is unable to determine the rate of tax or the value of goods. The proper officer can allow the assessee to pay tax on a provisional basis at a rate or a value which are specified by him.
Scrutiny Assessment:
The GST officer can scrutinize the returns in order to verify its correctness. The officer might ask for the explanation if he found any discrepancies in the returns.
Summary Assessments:
Summary assessment is done when the assessing officer go through the sufficient grounds to believe any delay in showing the tax liability can harm the interest of the revenue. To protect the interest of the revenue, he could pass the summary assessment with the prior permission from the Joint/Additional Commissioner.
Best Judgement Assessment:
Assessment – Non-filers returns:
If the registered taxable person doesn’t file his returns even after getting a notice, the officer would assess the tax liability to the best of his judgement using the relevant material.
Assessment – Unregistered persons:
When a taxable person fails to obtain the registration even though he is liable to do so, then the assessment is done.
To the Best of the judgement, the officer will assess the tax liability of such persons. The show cause notice will be received by the taxable person and he gets the opportunity of being heard.
Demand and Recovery:
This would be applicable when a registered dealer not paid the tax or paid the tax incorrectly, it is also applicable for the incorrect Input Tax Credit (ITC) or refund is claimed by the dealer.
The officer issues a show cause notice along with the demand for payment of tax and penalty if in a case of fraud.
Demands can arise in the following cases. They are:
- Tax have been collected but not deposited with the central or state government.
- Short paid tax or unpaid or wrong refund.
- SGST/CGST paid when IGST was payable and vice versa.
IT department starts the recovery proceedings if the demand is not paid.
Advance Ruling:
Before starting the proposed activity, for certain tax matters, seeks clarification from GST authority. This may help to reduce the costly litigation. Advance ruling is a written decision which has been given by the tax authority to the concerned applicant on the queries related to the supply of goods or services.
What is an advanced ruling?
An advanced tax ruling is a written interpretation of tax laws which is issued by the tax authorities to corporations and individuals. They are the ones who request for clarification on certain tax matters. This may be requested when the tax payer is confused or uncertain about certain provisions. It is applied for the advanced ruling before starts the proposed activity.
Under income tax, advance ruling is available in international taxation. This helps the non-residents to ascertain the tax liability, plan their income tax in advance, and avoid long drawn and costly legal disputes.
One of the leading business service providers, “Solubilis Corporate Services”, who provides efficient and reliable services to the clients as per their business related requirements. For more information -> Click here.

